The ones that are good and the ones to avoid.
No, not chocolate chip or sugar cookie, we're talking about HTTP cookies. These cookies, otherwise known as web cookies, are little bits of data that are collected by a website and saved in a tiny file on your computer and on the website’s server. Originally created in 1994 as a solution for making online shopping carts possible, the first application of cookies was on the Netscape website to determine whether a user had previously visited the website. Today, their purpose is to enhance your overall web browsing experience by remembering your recent activity, and tailoring your web experience to you.
Prior to the media’s exposé on web cookies in 1996, cookies were accepted by default and people had no idea of their existence. Once people became aware, web cookies became a major topic of discussion as a digital villain invading everyone's privacy. While the fear of cookies invading privacy is valid for some in some instances, some cookies actually benefit the user while browsing the internet. Some web cookies contribute to the User Experience (UX) making web browsing as easy as it is today. For example, cookies are the reason e-commerce websites will remember your shopping cart when you return to a site where you never checked out. Additionally, websites can use cookies to cross reference your activity with other users who had similar activity, allowing them to create recommendations such as "Customers Also Viewed" on e-commerce sites, "Suggested Content" on video streaming platforms, or "Related Searches" in search engine sites.
How Cookies Work
Every time you connect to a website, the site will search their server for any existing cookie data. Your first time visiting a website, since there is no cookie data stored yet, your web browser connects to the website and a small file is created on the website's server to save your activity and preferences. That file is also saved within your web browser on your computer. Typically a website creates a unique anonymous identifier to remember you rather than storing personal information on the server; however, if you enter in personal information on the website, this information is typically encrypted and stored within the unique cookie id.
The next visit, and any future visits to that website, your cookie data will be found in the site's initial search of their server, allowing your preferences, unpaid items in a shopping cart or login information to load automatically. Any new activity or preferences set while visiting the site is then saved to your cookie file for the next time you visit.
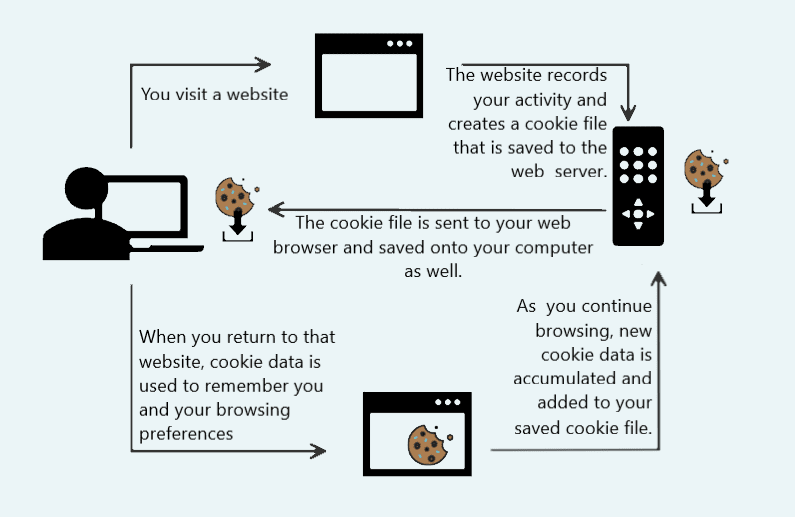
How cookies are made.
How cookies are made.
How cookies are made.
Type of Cookies
There are two main types of web cookies: session cookies & persistent cookies.
Session Cookies are temporarily stored in the web browser’s memory and deleted when the web browser is closed. These types of cookies are typically used to power an e-commerce website by remembering the items in your shopping cart, even if you leave the website. Additionally, they will save any specific preferences you’ve set on a website such as language or location. These cookies are more helpful than harmful and upon closing your web browser, the cookie data is deleted.
Persistent Cookies are stored for longer time periods within the web browser and remain intact even if the browser is closed; however, they typically have an expiration date. These types of cookies are utilized every time the user visits that website. Typically, this type of cookie allows a website to remember a specific device and user login, making the login process a bit easier. For example, many banks include an option to remember your account when logging into an online banking account on a specific device. If the user checks this box, the bank will not require the tedious multi-factor authentication or answers to security questions every time the user logs in to their bank account on that one device. Below are three different banks that allow users to opt-in to using persistent cookies on their devices.
Examples of frequently used persistent cookies
Examples of frequently used persistent cookies
Cookie Issuers
Cookies are either created by a first-party issuer or third-party issuer.
First-Party Cookies are created by the website that you are currently visiting. Many websites offer a cookie preference tab that lets the user choose the cookies they want turned on. Some cookies are essential to utilizing the web page which cannot be turned off, while others like analytics or marketing cookies can be turned off. These types of cookies are used by the company to track the effectiveness of the site's user experience or of a marketing campaign and are typically separated from any personally identifiable information.
Third-Party Cookies are cookies created by a website that you are not currently visiting—they typically come from online advertisements so companies can track what website a user was visiting when they clicked on the ad. If there is an ad on the website, it is likely that the ad owner and whoever else sells the digital ad space have cookies enabled for tracking the user's activity. These are typically persistent cookies that stay on the computer and track the user's long term activity. Since Google is one of the major digital advertisement providers, Google is tracking the long term activity on a user's web browser. While it may seem like an invasion of privacy, the reason for tracking a user's activity is to provide them with a tailored ad experience where ads the user sees are relevant to their searches and internet activity.
Cookie Stealing
There are a few different methods a hacker can utilize to steal a user’s cookie data; however, they are very complex and not frequently used. The best way to protect yourself from cookie fraud is to keep your web browser up to date. Most web browsers update automatically; however, if yours does not, make sure to be regularly checking for updates because in doing so,you are ensuring your web browser has the most up-to-date security.
Privacy
Typically, first-party and session cookies pose little risk to privacy concerns; however, persistent and third-party cookies are relatively invasive of individuals’ privacy. Since many advertisements on websites are powered by Google Adsense, Analytics, Maps, etc, the collected cookies provide Google with your internet activity. While marketing professionals will argue that the collected cookies help tailor advertisements to the user, the information collected by third-party cookies give people a justified concern about their privacy.
Fortunately, browsers allow users to manage their cookie settings. On a desktop computer, Google Chrome, Firefox, Edge and Internet Explorer all offer cookie settings. Mobile devices also offer cookie settings within Apple iOS Safari, Chrome, Android's built in browsers and Blackberry's web browser. Since each browser is a little different there is not one process for turning the cookies off; however, a simple Google search of, "[Your Browser] Manage Cookie Preferences" will give you a list of articles explaining the process. Ultimately,there is no way around cookies, but managing the settings in your browser will help significantly with websites creating cookie files to collect your web activity, preferences or account information.